Dental veneers, while celebrated for their ability to transform smiles by covering discolored or damaged teeth, may not provide an all-encompassing solution for all dental concerns, such as receding gums. Since veneers are designed to enhance the aesthetic appeal of teeth rather than address periodontal issues, can they effectively cover receding gums? The relationship between veneers and gum health is more complex and warrants a deeper exploration to fully understand the limitations and potential alternatives for treating gum recession.
Understanding Receding Gums
Gum recession is a prevalent dental ailment that demands a thorough understanding. This condition, characterized by the gradual withdrawal of the gum tissue, exposes more of the tooth or the tooth’s root. It’s a potentially serious issue that can lead to additional dental health dilemmas if left untreated.
Gum health is a critical aspect of oral hygiene, often overlooked. Receding gums can be a sign of gum disease, the result of aggressive brushing or genetic predisposition. Symptoms may include sensitive teeth, visible tooth root, longer-looking teeth, and discomfort or inflammation of the gum tissue.
Regarding treatment options, they vary based on the severity of the recession. Mild cases may only require a more rigorous oral care regimen, including a softer brushing technique and therapeutic mouthwash. However, severe recession may necessitate surgical procedures like gum grafts, pocket depth reduction, or regeneration of lost bone and tissue.
Understanding the causes and symptoms of gum recession is instrumental in maintaining peak gum health. Prompt identification and treatment can help prevent further damage, tooth loss, and enhance overall dental health. The significance of this issue warrants extensive awareness and proactive measures to mitigate its impact.
What Are Dental Veneers?
Moving on from the topic of receding gums to another important aspect of dental health, we now turn our attention to dental veneers. A notable development in the field of cosmetic dentistry, dental veneers have revolutionized the way people can achieve an aesthetic enhancement of their smile.
Dental veneers, commonly made from porcelain or composite resin, are thin shells that are custom-fitted and bonded to the front surface of teeth. They are a popular choice for addressing a variety of dental issues, such as discolored, chipped, misaligned, or gap-filled teeth. The veneers are meticulously crafted to match the color, shape, and size of the patient’s natural teeth, ensuring a natural-looking and harmonious smile.
Dental veneers offer a conservative approach to changing a tooth’s color and shape without the need for extensive shaping procedures that crowns require, hence preserving the natural tooth structure. With proper care, these veneers can last for many years, providing a durable and long-lasting option for those seeking to enhance their smile. So, while dental veneers are primarily used for aesthetic purposes, they also contribute notably to dental health by protecting the surface of damaged teeth.
Veneers and Gum Recession: The Connection
A considerable relationship exists between dental veneers and gum recession, a common dental problem that affects many individuals worldwide. Dental veneers, particularly porcelain and composite resin types, are custom-designed shells applied to the front surface of teeth to improve their appearance. However, their installation and maintenance can inadvertently impact gum health, possibly leading to gum recession.
The process of affixing veneers involves trimming the enamel, a procedure that can sometimes irritate the gums, causing them to recede. Additionally, poor oral hygiene post-installation can also lead to gum inflammation and eventually recession, as the veneers may harbor bacteria if not properly cleaned. Consequently, while veneers are an effective solution for aesthetic dental issues, they can potentially contribute to gum recession.
It is essential to understand that veneers can neither cause nor prevent gum recession independently. Other factors such as genetic predisposition, aggressive tooth brushing, and periodontal diseases also greatly influence gum health. As a result, while considering veneer types, one must also consider their potential impact on gum health. Regular check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene are imperative to guarantee healthy gums while enjoying the benefits of dental veneers.
Limitations of Veneers for Gum Recession
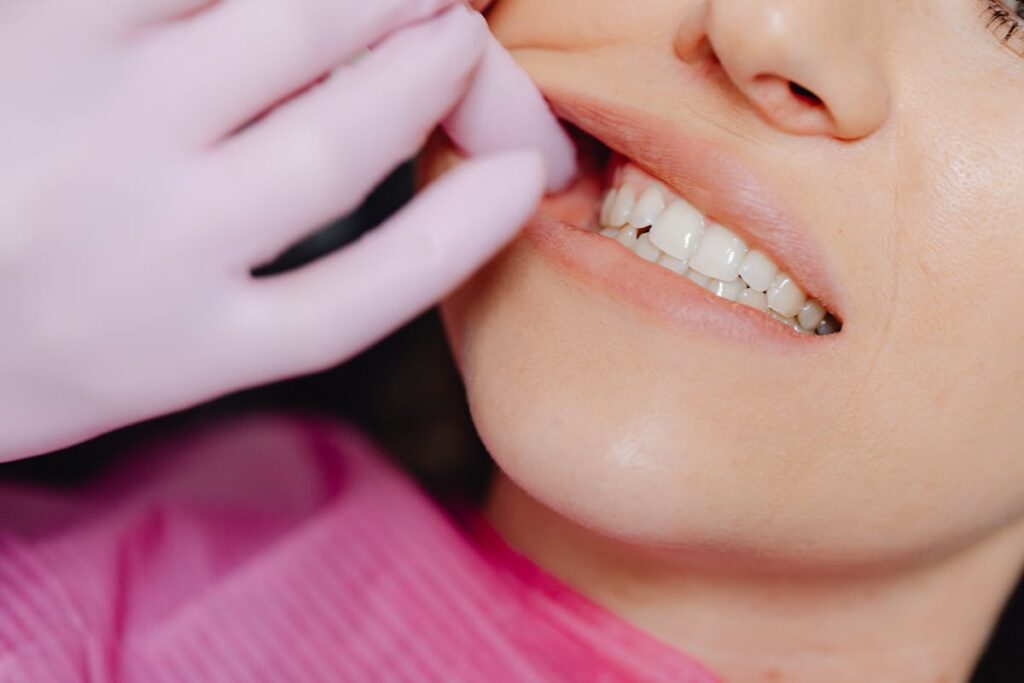
While veneers can offer an aesthetic solution for teeth affected by gum recession, they are not without their limitations. This form of treatment, though effective in masking dental imperfections, may fail to directly address the underlying issue of receding gums. We will further explore these constraints, the recurring issues with gum recession, and potential alternative treatments in the subsequent discussion.
Understanding Veneers’ Role
One must comprehend that while veneers can greatly enhance the appearance of your teeth, they do have limitations when it comes to gum recession. The main role of veneers is to provide aesthetic enhancement for the front surface of teeth. They are, fundamentally, a cosmetic solution designed to improve the color, shape, size, or length of teeth. There are undeniable veneers benefits, such as resistance to stains and the ability to closely mimic the light reflecting properties of natural teeth.
However, veneers are not designed to cover or treat gum recession. They are affixed to the tooth’s surface, and won’t extend to the gum line if it has receded. Consequently, while veneers can camouflage minor gum recession, in the case of severe gum recession, they fall short of providing an all-encompassing solution.
It is important to understand that veneers are fundamentally a cosmetic solution, their role in dealing with gum recession is limited. Consequently, patients with receding gums should consult with their dentist or a periodontist to discuss more suitable options for treating their gums while considering veneers for aesthetic enhancement.
Receding Gums Dilemma
Despite the aesthetic benefits of veneers, their limitations become apparent when faced with the issue of receding gums. Veneers, a cosmetic dentistry innovation, are designed to mask dental imperfections by replicating the natural look of teeth. However, they are not equipped to address gum recession or gum disease, a common condition often associated with ageing, poor oral hygiene, or genetics.
When gums recede, they expose more of the tooth’s root, creating gaps where disease-causing bacteria can grow. Veneers merely cover the front surface of teeth, leaving these exposed areas unprotected. This limitation not only fails to address the cause of the problem, but it also puts patients at risk for further dental complications.
Moreover, veneers require a certain amount of healthy gum tissue for proper placement and longevity. Gum recession can compromise this requirement, leading to poor fit, discomfort, or even failure of the veneers over time. In such scenarios, veneers can exacerbate issues rather than solve them.
Alternative Treatment Options
Given the limitations of veneers in handling gum recession, alternative treatment options must be considered. Gum grafting, a surgical procedure that utilizes a patient’s own tissue or a synthetic material to cover exposed root surfaces, is a common and effective method of treating gum recession. This procedure can considerably improve both oral health and aesthetics.
Another alternative is laser therapy, an increasingly popular, minimally invasive treatment that stimulates tissue regeneration and promotes healing. It can be used in conjunction with other treatments such as scaling and root planning for thorough periodontal maintenance.
Orthodontic treatment can also play a vital role, especially when misalignment contributes to gum recession. By correcting the position of the teeth, the gums are better able to adhere and provide protection. Restorative dentistry, including crowns and bridges, can further aid in maintaining gum health.
Preventative care, like regular dental check-ups and proper oral hygiene, is paramount in managing gum recession. It also helps identify potential problems early, allowing for timely intervention. While veneers may offer aesthetic solutions, it’s essential to address the root cause of gum recession to achieve long-lasting, healthy results.
Alternative Treatments for Receding Gums
A significant number of individuals with receding gums often seek alternative treatments to conventional methods. These alternatives aim to manage the condition adequately and restore oral health without the need for extensive surgical procedures.
One such alternative treatment is laser therapy. This innovative technique uses concentrated light energy to remove diseased tissue, promote the formation of new, healthy gum tissue and encourage overall oral health. Laser therapy is non-invasive and often results in less discomfort and a shorter recovery period than traditional surgical methods.
Another viable treatment option is gum grafting. This procedure involves transplanting soft tissue, usually from the roof of the mouth, to the affected area, thereby covering exposed roots and reducing sensitivity. This method not only improves oral health but also enhances aesthetic appearance.
Regenerative techniques are also gaining popularity. These involve the use of membranes, grafting material, or tissue-stimulating proteins to encourage the body’s natural ability to regenerate healthy gum tissue.
Lastly, periodontal maintenance is key to managing receding gums. Regular dental cleanings and check-ups can help maintain oral health, prevent further recession, and monitor the success of alternative treatments.
The Role of Dental Hygiene
While exploring various treatments for receding gums, it becomes apparent that prevention plays a significant role in maintaining oral health. Dental hygiene, especially, is a vital aspect of prevention. Regular and effective dental care can help avoid many oral health issues, including receding gums.
Oral hygiene is not just about brushing your teeth twice a day; it encompasses a holistic approach that includes flossing, using mouthwash, and regular dental check-ups. Brushing removes the plaque buildup, which is the main culprit behind gum diseases. Flossing assists in removing food particles and bacteria that are often missed during brushing, especially between the teeth. Mouthwash can kill bacteria that cause gum diseases, thereby preventing the gums from receding.
A balanced diet is another important aspect of dental care. Consuming foods rich in calcium and vitamin C can strengthen your gums and teeth. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can accelerate gum recession, so these habits should be avoided for ideal oral health.
Consulting Your Dentist: The First Step
One might underestimate the importance of scheduling regular visits with their dentist. However, when it comes to managing oral health issues such as receding gums, the need for professional consultation cannot be overstressed. Engaging with a knowledgeable dentist at an early stage can greatly influence the success of gum restoration efforts.
In the area of cosmetic dentistry, dentists can provide a thorough analysis of your oral health status while evaluating the best possible treatments tailored to your needs. Veneers, for instance, are a widely used cosmetic solution, but their suitability for each individual case varies. Depending on the extent of gum recession and overall oral health, veneers may or may not be the best solution.
Moreover, dentists provide essential advice on preventative measures and maintenance techniques. To guarantee the longevity of treatments such as veneers, proper oral hygiene and regular follow-up visits are vital. Dentists can offer guidance on maintaining your veneers and preventing further gum recession.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Average Cost of Getting Dental Veneers?
The average cost of dental veneers varies depending on veneer types and materials used. Porcelain veneers typically cost between $925-$2,500 per tooth, while composite resin veneers are usually less expensive, ranging from $250-$1500 per tooth.
How Long Do Veneers Typically Last?
Veneer longevity factors include oral hygiene and dental habits. With proper care, veneer lifespan expectations range from 10-15 years. However, more durable materials like porcelain can extend this lifespan up to 20 years or more.
Can Veneers Be Replaced or Repaired if Damaged?
Yes, damaged veneers can indeed be replaced or repaired. Several veneer replacement options and veneer damage solutions exist, ensuring the restoration of a natural, aesthetically pleasing smile irrespective of the initial damage sustained.
Do Veneers Require Any Special Care or Maintenance?
Veneers do require special care to maintain their aesthetics. Key veneer hygiene tips include regular brushing, flossing, avoiding hard foods, and scheduling periodic dental check-ups to guarantee their longevity and continued good appearance.
Will Insurance Cover the Cost of Veneers?
Insurance coverage for veneers can vary greatly depending on your insurance provider and the specific type of veneer. It’s crucial to consult with your insurance company to understand the extent of coverage they provide for veneers.