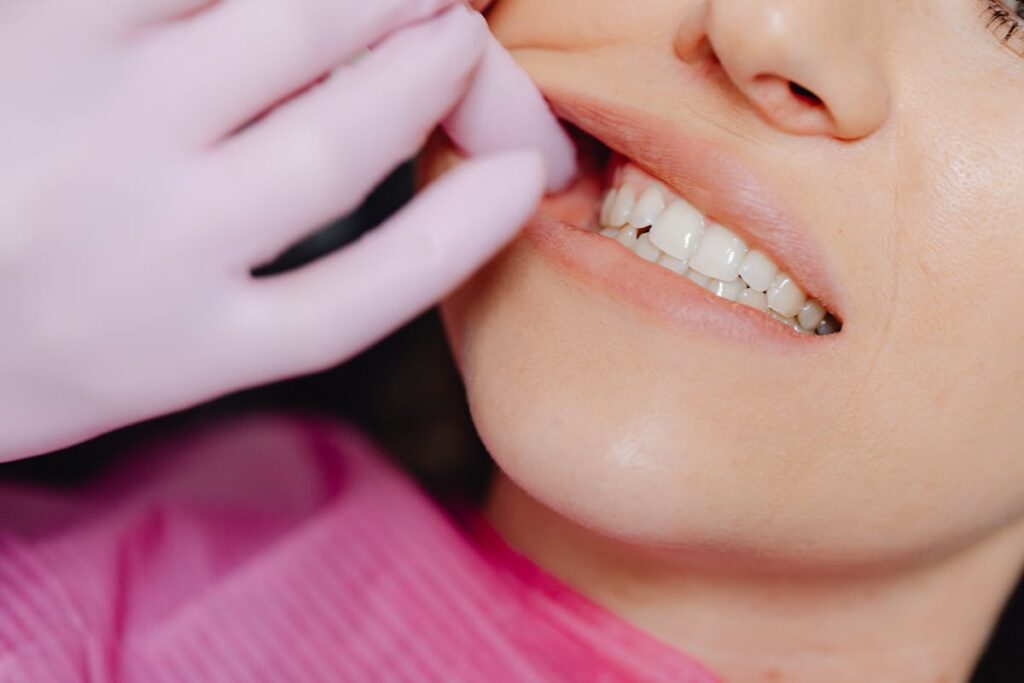
The correlation between diabetes and oral health complications, specifically bleeding gums, is a multifaceted issue that necessitates further exploration. It is known that diabetes can intensify the severity of gum diseases due to the body’s impaired ability to combat infections. However, the intriguing aspect is the reciprocal nature of this relationship – poor oral health can also exacerbate diabetes control. This intricate interplay invites a deeper exploration into the management of diabetes from an oral health perspective, a facet often overlooked in traditional diabetes care.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Complications
One cannot overstate the profound impact diabetes can have on an individual’s overall health. This chronic disease is characterized by prolonged periods of elevated blood sugar levels, which can lead to a range of complications if not adequately managed. Two primary types of diabetes exist: Type 1, an autoimmune condition where the body does not produce insulin, and Type 2, resulting from the body’s development of insulin resistance.
Insulin resistance, a vital factor in Type 2 diabetes, occurs when cells in muscles, fat, and liver resist or ignore the signal that the hormone insulin is sending out, which is to grab glucose out of the bloodstream and put it into our cells. This resistance subsequently causes a buildup of glucose in the blood, elevating blood sugar levels.
Over time, high blood sugar levels can cause damage to various body systems, leading to complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Additionally, diabetes has been found to impact oral health considerably, leading to conditions such as gum inflammation and bleeding gums. As a result, understanding the intricacies of diabetes and its related complications is essential for effective management.
Link Between Diabetes and Gum Disease
The relationship between diabetes and oral health complications, particularly gum disease, is a fascinating and complex aspect of this chronic condition. The body’s ability to resist infection is impaired due to high blood glucose levels, which is a common characteristic of diabetes. Consequently, the gums are more susceptible to bacterial invasion, leading to periodontal disease.
There is a bidirectional relationship between diabetes and gum disease. Poorly managed diabetes can lead to severe gum disease, and conversely, serious gum disease can affect blood glucose control and contribute to the progression of diabetes. This association highlights the importance of effective diabetes management and oral hygiene in preventing these complications.
A cornerstone of diabetes management is maintaining good oral hygiene. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are essential. Research shows that diabetics who practice good oral hygiene can help control their blood sugar levels, reducing their risk of gum disease.
Reasons for Bleeding Gums in Diabetics
Within the diabetic population, bleeding gums emerge as a prevalent oral health issue, the roots of which can be traced to specific factors linked to diabetes. To understand this, we must first scrutinize the impact of diabetes on gum health, specifically its role in altering the oral environment. Additionally, we will examine the correlation between diabetes and gingivitis, a common gum disease often marked by bleeding gums.
Diabetes’ Impact on Gums
Bearing the brunt of diabetes often extends beyond blood sugar control, as it can greatly affect oral health, particularly the gums. This interaction between systemic diabetes and oral conditions is a result of the body’s impaired ability to combat infections and promote healing.
Changes in blood glucose levels, a crucial element of diabetes management, can impact gum health considerably. Elevated blood glucose levels compromise the immune system, making it less effective in fighting off bacterial infection in the gum tissues. As a result, diabetics are more prone to developing periodontal disease, a severe form of gum infection.
Additionally, diabetes can lead to dry mouth due to decreased salivary flow. Saliva plays an essential role in eliminating food particles and neutralizing harmful acids in the mouth. Reduced saliva flow can result in gum inflammation and bleeding, increasing the risk of oral infections.
Correlation: Diabetes and Gingivitis
Why do diabetics often suffer from bleeding gums? The answer lies in the complex correlation between diabetes and gingivitis, a common oral health problem.
- Blood Sugar Levels: Elevated blood glucose levels, characteristic of diabetes, promote bacterial growth in the mouth. Bacteria are the primary cause of gingivitis symptoms such as gum inflammation and bleeding.
- Immune Response: Diabetes weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections, including gum disease.
- Blood Vessel Changes: Diabetes causes thickening of blood vessels, impairing the flow of nutrients to the gums and the removal of harmful waste products. This exacerbates gum inflammation and bleeding.
- Poor Diabetes Management: Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to severe gingivitis symptoms. Proper diabetes management, including blood sugar control, can help prevent these complications.
Impact of Oral Health on Diabetes Control
Have you ever considered the role your oral health might play in managing diabetes? Oral hygiene, often overlooked, is in fact a critical factor in achieving ideal blood sugar control.
Oral health serves as a mirror to our overall health status, reflecting conditions such as diabetes. Poor oral hygiene can lead to gum infections, and subsequently, the body’s inflammatory response. This inflammation can make it harder for insulin to do its job and regulate blood sugar. Hence, poor oral health can trigger a vicious cycle of high blood sugar levels, leading to more severe gum diseases and ultimately worsening the diabetes.
Practicing good oral hygiene, on the other hand, can help manage blood sugar levels. Regular brushing and flossing can prevent the formation of plaque, the primary cause of gum diseases. Controlling gum diseases can reduce the body’s need to produce insulin, thereby helping to control blood sugar levels.

Recognizing Symptoms of Gum Disease
Recognizing symptoms of gum disease is critical for individuals with diabetes, as this condition can impact gums adversely. It is important to understand the tell-tale signs of gum disease, such as redness, swelling, or bleeding, to seek early interventions. Additionally, understanding how to prevent and treat gum disease can greatly improve both oral health and diabetes management.
Identifying Gum Disease Signs
Even though gum disease may initially present with subtle symptoms, it’s essential for diabetics to be vigilant in identifying these early warning signs. Recognizing the onset of gum disease can be vital to maintaining good oral hygiene and overall health.
- Red, swollen gums: Healthy gums are typically pink and firm. Any deviation from this, such as redness, swelling, or tenderness, should be a cause for concern. These could be early signs of gum disease.
- Bleeding gums: If your gums bleed easily during brushing or flossing, it could be indicative of gum disease. Healthy gums should not bleed with regular oral hygiene practices.
- Persistent bad breath or bad taste: Chronic bad breath or a persistent bad taste in your mouth could be signs of gum disease. This is often due to bacteria and plaque buildup.
- Loose teeth or change in bite: Gum disease can cause the teeth to shift or become loose. If you notice a change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite, it could be a sign of advanced gum disease.
Diabetes’ Impact on Gums
The intricate relationship between diabetes and gum disease must not be overlooked. Diabetes, a systemic condition characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose, can notably impact oral health, particularly the health of the gums. This often manifests as gum inflammation, a key indicator of the onset of gum disease.
Studies have shown that individuals with poorly controlled diabetes are more susceptible to bacterial plaque, which contributes to the development of gum disease. This is primarily due to the hyperglycemic environment which creates ideal conditions for bacterial proliferation. Additionally, diabetes hampers the body’s response to infection, reducing the ability to control and eliminate the bacteria responsible for gum inflammation.
Oral hygiene plays a pivotal role in the management of this condition. Regular and effective oral care can notably reduce the level of bacterial plaque and subsequently, gum inflammation. However, in a diabetic individual, the importance of maintaining oral hygiene is amplified due to the increased vulnerability to gum disease.
Prevention and Treatment Options
In the battle against gum disease, early detection plays a vital role. Identifying symptoms promptly allows for swift intervention, maximizing the effectiveness of both preventive measures and treatment options. Prevention, which is rooted in solid dental hygiene practices and nutritional strategies, is the first line of defense against gum disease.
- Dental Hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing are fundamental. Using fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristle toothbrush can help to remove plaque and prevent gum infection. Regular dental checkups, including professional cleanings, are also essential.
- Nutritional strategies: A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can boost your gum health. Limit sugar intake to prevent bacterial growth and plaque buildup.
- Quit Smoking: Tobacco use increases the risk of gum disease considerably. Eliminating this habit can help to improve your oral health.
- Control Diabetes: High blood glucose levels can cause gum infections. Regular monitoring and control of blood sugar levels can help prevent gum disease.
When preventive measures aren’t enough, treatments such as scaling and root planing, antimicrobial therapy, or even surgery may be necessary. Always consult with your dental professional to determine the best course of action.
Preventative Measures for Oral Health
Maintaining robust oral health necessitates a proactive approach, particularly for individuals living with diabetes. Dental hygiene is paramount, and tooth brushing, coupled with effective flossing techniques, can drastically reduce the risk of gum disease. A well-selected mouthwash offers additional benefits, including the elimination of bacteria and plaque, which are common culprits behind gum inflammation.
Regular professional cleanings are also essential as they provide a more thorough cleanse than typical home care can achieve. These check-ups also allow for early detection of potential oral health issues, enabling timely intervention and treatment.
Dietary choices greatly impact oral health. Opting for sugar substitutes can lower the risk of tooth decay, a common concern among diabetics. Moreover, the importance of hydration cannot be overemphasized. Drinking sufficient water promotes salivary flow, which naturally cleanses the mouth and helps in maintaining a balanced oral pH.
Stress management is another critical aspect of preventative oral health care. Chronic stress can compromise the immune system, making the gums more susceptible to infection. Consequently, incorporating stress management techniques can indirectly contribute to maintaining healthy gums. To sum up, a thorough approach, including proper dental hygiene and lifestyle modifications, can greatly improve oral health among diabetics.
Managing Diabetes to Improve Gum Health
While preventative measures for oral health greatly contribute to the reduction of gum inflammation and disease, achieving ideal gum health is closely tied to effective diabetes management. Understanding the symbiotic relationship between diabetes and oral hygiene is vital to maintaining optimal health.
- Blood Sugar Control: Regular monitoring and control of blood glucose levels decrease the likelihood of gum disease and other oral health complications. Maintaining a balanced diet and making necessary dietary adjustments is a key step in this process.
- Oral Hygiene: Regular and proper brushing, flossing, and use of an antiseptic mouthwash can prevent plaque buildup, a major contributor to gum disease. Regular dental check-ups are also essential for early detection and treatment of any potential issues.
- Dietary Adjustments: Consuming a balanced diet low in sugar and high in fiber can have a considerable impact on blood sugar levels. It also promotes healthier gums and teeth.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can help regulate blood sugar levels, thereby reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications, including gum disease.
Effectively managing diabetes requires a thorough approach that includes good oral hygiene and dietary adjustments. By taking these steps, you can greatly improve your oral health and overall wellbeing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Diabetes Be Diagnosed Through Oral Health Checks?
While oral health checks can reveal signs of potential systemic diseases, they alone cannot definitively diagnose diabetes. However, there’s a notable correlation between poor oral health, particularly periodontal disease, and the presence of diabetes.
Does Insurance Cover Dental Treatments for Diabetes-Related Gum Disease?
Insurance coverage varies widely. Some plans may cover dental treatments related to gum disease, while others may not. It is essential to review your specific policy or consult with your insurance provider for accurate information.
Are Bleeding Gums a Sign of Prediabetes?
Yes, bleeding gums can be a symptom of prediabetes. Poor gum health, including inflammation and bleeding, may indicate insulin resistance. However, multiple symptoms should be considered for an accurate prediabetes diagnosis. Consult a healthcare professional.
Does Managing Gum Disease Help to Reduce Blood Sugar Levels?
Effective management of gum disease can contribute to the reduction of blood sugar levels. Gum infection control reduces systemic inflammation, thereby potentially improving glycemic control in individuals with persistent high blood sugar levels.
Can Diabetes Medications Cause Gum Problems?
Yes, certain diabetes medications can potentially impact gum health, leading to issues such as gum inflammation and bleeding. It’s essential for individuals on these medications to maintain diligent oral hygiene to prevent such complications.