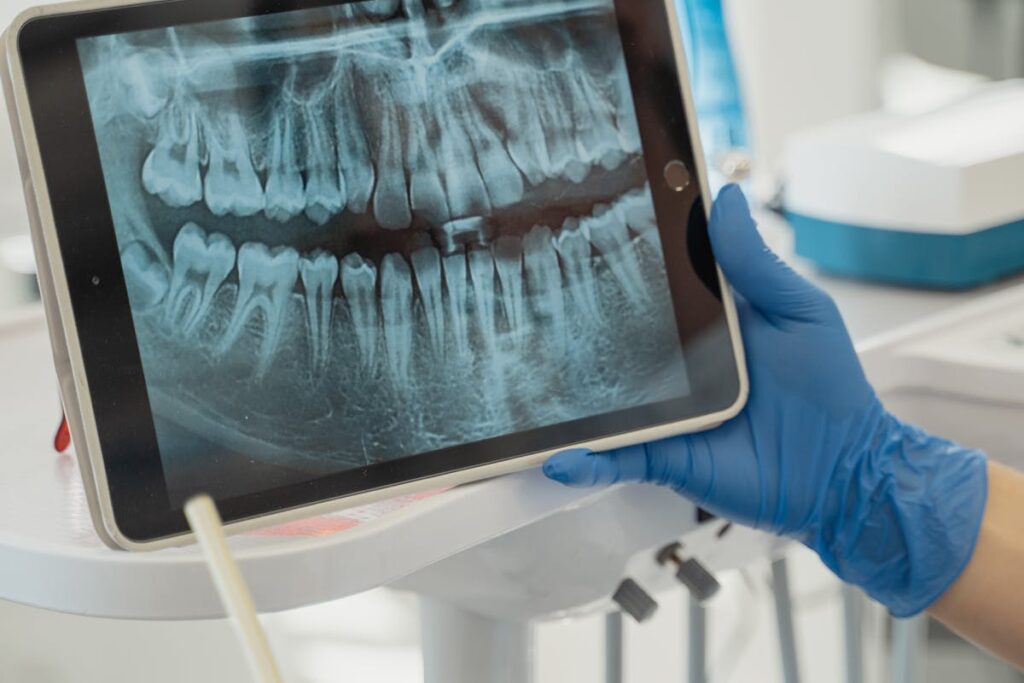
The role of dental X-rays in the prevention of major oral health issues is indeed profound. As an indispensable tool in modern dentistry, X-rays provide valuable insights that go beyond the reach of routine dental examinations, enabling dentists to diagnose and treat potential problems at their nascent stages. However, the question arises – are these benefits worth the risks associated with radiation exposure? And does the frequency of these X-rays have an impact on their effectiveness in preventing oral health issues? Let us explore these queries further.
Understanding Dental X-Rays
Peering beneath the visible surface of the teeth and gums, dental X-rays provide an indispensable diagnostic tool for dentists. This form of imaging utilizes dental X-ray technology to generate detailed images of the oral cavity. These images allow dentists to identify issues like hidden dental structures, malignant or benign masses, bone loss, and cavities that may not be detectable through a standard visual examination.
Radiation safety is a paramount concern in the application of dental X-ray technology. Fortunately, advancements in this field have led to noticeably reduced radiation exposure. Modern dental X-ray machines are equipped with high-speed film, digital X-ray sensors, and protective aprons and collars, all designed to minimize radiation exposure and guarantee patient safety.
Dental X-rays play a critical role in preventive dental care. They enable early detection of oral health issues, facilitating timely treatment and potentially preventing the development of more serious conditions. Consequently, they are a key component of thorough dental examinations. It is worth noting that the frequency and type of X-ray needed will vary depending on the patient’s individual health history and current oral health condition.
The Importance of Early Detection
Highlighting the importance of early detection in oral health management, dental X-rays serve as an essential diagnostic tool. They aid in the early diagnosis of potential dental issues that may otherwise remain undetected, leading to complicated conditions. By identifying problems at the onset, dental X-rays pave the way for timely intervention and preventive care, which can greatly enhance oral health outcomes.
Early detection can reveal minor issues such as cavities and tooth decay, which, if ignored, can eventually lead to severe discomfort and even tooth loss. Dental X-rays can also detect more serious conditions such as bone loss, tumors, and cysts that are not visible to the naked eye during routine oral examinations.
Incorporating dental X-rays into routine dental check-ups plays a crucial role in preventive care, reducing the risk of major dental issues in the future. This proactive approach not only helps in maintaining a healthy oral cavity but also minimizes the financial burden associated with major dental procedures. Therefore, dental X-rays in conjunction with regular dental check-ups provide thorough oral health care, emphasizing the essential role of early detection.
Types of Dental X-Rays
In examining dental X-rays and their role in oral health, it is essential to differentiate between the various kinds available. Two significant types, which will be the focus of our discussion, are Bitewing and Panoramic X-Rays. These respective modalities offer distinct advantages and applications in the field of dentistry, and a thorough understanding of each will enhance our extensive overview of dental radiography.
Bitewing X-Rays Explained
Understanding the various types of dental X-rays can greatly enhance a patient’s knowledge and comfort when it comes to dental health. Bitewing X-rays are a common type, named so because the patient must bite down on a wing-shaped device while the images are captured.
The bitewing benefits are manifold, primarily because they provide a detailed view of the upper and lower teeth in one area of the mouth, allowing dentists to detect decay between teeth and changes in bone density. Bitewing X-rays are also useful for tracking teeth growth and development in children and teenagers. Furthermore, they are essential in identifying early stages of gum disease by revealing bone loss.
However, bitewing X-rays also have their limitations. They only capture a specific section of the mouth, not the entire oral structure, making them less ideal for evaluating jaw problems or impacted teeth. Also, bitewing X-rays may not be suitable for patients who have difficulty keeping still or those with a sensitive gag reflex, as the wing-shaped device must be held in place by biting down.
Panoramic X-Rays Uncovered
Shifting our focus to another type of dental X-ray, we uncover the panoramic X-ray. A distinctive tool in dental diagnostics, the panoramic X-ray employs advanced panoramic techniques to capture an extensive view of the oral cavity. Unlike other dental X-rays that focus on specific areas, it provides an overall snapshot of the teeth, jawbones, sinuses, and surrounding structures.
One of the panoramic advantages is its ability to detect problems that localized X-rays may overlook. They are often used to plan treatment for dental implants, detect impacted wisdom teeth and jaw abnormalities, and diagnose tumors. Panoramic X-rays can also reveal early stages of gum disease and bone loss that are not visible during a regular dental examination.
Furthermore, panoramic X-rays expose patients to less radiation compared to traditional methods. The procedure is quick, comfortable, and highly efficient, making it a preferred choice for dentists and patients alike. However, it is essential to recognize that while panoramic X-rays provide a broad view, more detailed images might be needed for accurate diagnosis of specific issues.
What Dental X-Rays Reveal
A staggering 90% of systemic diseases have oral manifestations that may be detected by dental X-rays. These imaging techniques provide invaluable insights into the hidden aspects of oral health, thereby enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Dental X-rays reveal both the external and internal structure of teeth, including roots hidden under the gums, and the jawbone. This information is critical in identifying problems that are not visible to the naked eye, such as tooth decay, impacted teeth, abscesses, and bone loss.
The information garnered from dental X-rays plays an essential role in treatment planning. For instance, they help dentists determine the appropriate course of action in complex procedures such as root canal treatment, tooth extractions, and placement of dental implants. Additionally, X-rays can reveal the early stages of oral health issues like gum disease, enabling preventative measures before the condition exacerbates.
In children, dental X-rays are instrumental in monitoring tooth growth and development, helping dentists to anticipate potential issues that could impact the alignment of teeth or the formation of the jaw.
In essence, the revelations from dental X-rays offer an all-encompassing view of oral health, enabling personalized and effective treatment, which is crucial in preventing major oral health issues.
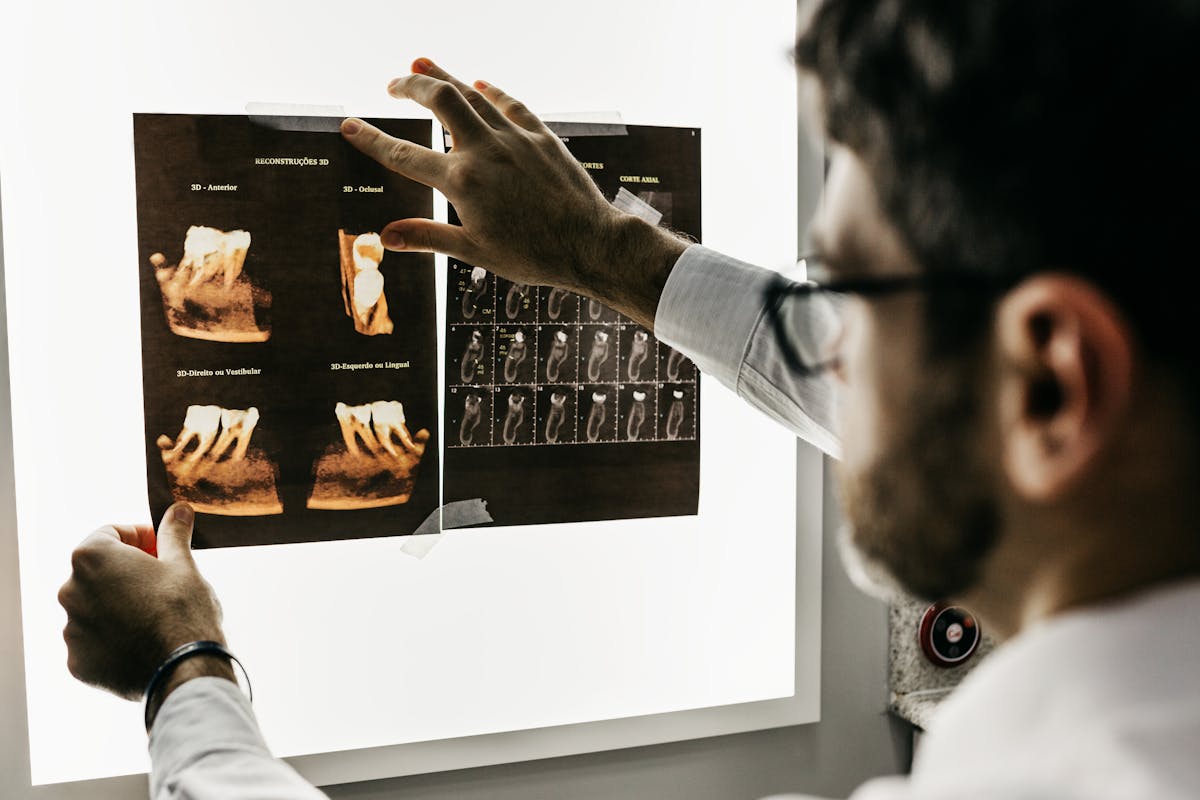
Dental X-Rays and Oral Diseases
With the aid of dental X-rays, a variety of oral diseases can be detected even before they present noticeable symptoms. This advanced x-ray technology plays an essential role in oral disease prevention, enabling dentists to diagnose and treat conditions early, thereby mitigating risks of further complications.
Dental X-rays can identify tooth decay hidden between teeth or under existing fillings and crowns that are not visible during a standard oral examination. They also detect bone loss associated with gum disease, a severe oral condition that can lead to tooth loss if not treated promptly. In addition, these X-rays can highlight changes in the bone or root canal that could indicate a potential infection or abscess.
Moreover, dental X-rays help in the detection of cysts, tumors, and other abnormalities within the oral structures, potentially leading to early diagnosis of oral cancer. Early detection is key in managing these diseases effectively, and can drastically improve prognosis.
In essence, x-ray technology provides a thorough view of one’s oral health, acting as an indispensable tool in the prevention, early detection, and management of oral diseases. Its role in preserving oral health is undeniably significant, making regular dental X-rays an essential part of routine dental care.
Risks and Benefits of Dental X-Rays
As we further explore the topic of dental X-rays and oral health, it is essential to understand both the risks and benefits associated with this common dental procedure. Dental X-rays, while instrumental in diagnosing and treating oral diseases, also carry certain risks, primarily due to radiation exposure. However, with advancements in dental technology, these risks are continually being minimized, making it vital to balance the potential dangers with the undeniable health benefits.
Understanding Dental X-Ray Risks
Maneuvering the world of dental care often involves understanding the potential risks and benefits of various procedures, including dental X-rays. One of the most significant risks associated with dental X-rays is radiation exposure. It is important to note that while X-rays do emit a low level of radiation, prolonged or frequent exposure can potentially lead to harmful effects.
The degree of radiation exposure largely depends on the type of X-ray procedure conducted. For instance, bitewing X-rays, which are commonly used to detect cavities between teeth, expose patients to a minimal dose of radiation. On the other hand, more thorough exams, like full-mouth series or panoramic X-rays, involve a slightly higher level of radiation exposure.
Despite these risks, dental professionals adhere to strict safety protocols to mitigate the effects of radiation. These protocols include the use of lead aprons and thyroid collars to protect sensitive body parts. In addition, modern dental X-ray machines are designed to limit the radiation beam to the small area being X-rayed.
Benefits of Dental X-Rays
Despite the potential risks, dental X-rays offer a multitude of benefits vital in maintaining ideal oral health. The primary advantage lies in the high diagnostic accuracy of these tools. Dental X-rays provide a thorough and precise view of the mouth, enabling dentists to identify issues that might otherwise be invisible to the naked eye.
These include cavities hidden between teeth, infections lurking in the roots, and bone loss associated with gum disease. The early detection of such conditions is essential in initiating prompt and effective treatment, preventing their progression into more severe, potentially debilitating oral health issues.
Furthermore, dental X-rays enhance patient comfort. By providing clear images of the mouth structure, they guide practitioners in planning procedures, minimizing the need for invasive exploratory processes. This results in less chair-time, reducing patient stress and discomfort. In pediatric cases, the comfort and speed delivered by dental X-rays greatly contribute to a positive dental experience, fostering an attitude of regular dental care from an early age.
Balancing Risks and Benefits
Maneuvering the balance between the risks and benefits of dental X-rays is an essential endeavor for both healthcare providers and patients. The process involves a careful risk assessment and a thorough benefit analysis, both of which should be undertaken with a patient-centered approach.
Risk assessment primarily refers to evaluating the potential harm that could come from exposure to the radiation in dental X-rays. While the radiation levels are low, repeated exposure can potentially increase the risk of certain cancers and other health issues. Consequently, it’s imperative for health professionals to limit the frequency of X-rays to only when necessary, and to utilize protective measures such as leaded aprons and collars.
On the other side of the balance is the benefit analysis. Dental X-rays play a significant role in diagnosing and managing a multitude of oral health issues, from cavities and gum disease to oral cancers. They offer detailed images of the teeth and surrounding structures, allowing for early detection and prevention of further complications.
Frequency of Dental X-Rays
While it’s common to receive dental X-rays during routine check-ups, the frequency of these X-rays can vary considerably depending on your oral health status and risk factors. The American Dental Association (ADA) provides frequency guidelines that help dental professionals determine the appropriate x-ray intervals for patients.
These guidelines are not fixed but are subject to individual patient considerations. For example, a patient with a history of numerous dental procedures and recurring issues might require more frequent X-rays to monitor their oral health. Conversely, a patient with excellent oral health and no history of dental disease might have X-rays less frequently.
The frequency of dental X-rays can also be influenced by the patient’s age, with different guidelines for children, teens, adults, and seniors. It’s important to remember that these guidelines serve as a baseline and your dentist may adjust the frequency based on your specific oral health needs.
Dental X-Rays in Children and Adults
Building on the understanding that the frequency of dental X-rays can vary with age, it is equally important to examine the specifics of dental X-rays in both children and adults. The pediatric considerations come into play due to the unique characteristics of a child’s growing and developing mouth. Children have a higher susceptibility to dental caries, therefore requiring more frequent X-rays. The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends that children at high risk should have X-rays every six months.
On the other hand, adult screenings can be more spread out. The frequency of X-rays for adults is typically determined by the individual’s oral health status, with those presenting a higher risk of dental disease necessitating more frequent X-rays. For adults with good oral health and not at risk for cavities or gum disease, a dental X-ray every two to three years is generally sufficient.
Understanding the specific needs of different age groups allows for a more personalized approach to dental health, ensuring that each individual receives the most suitable care. Dental X-rays play an essential role in preventive care and early detection, ultimately aiding in maintaining peak oral health for both children and adults.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Dental X-Rays Detect Conditions Outside of Oral Health Issues?
Yes, dental X-rays can detect conditions beyond oral health issues, including sinus infections and certain types of tumors. However, the benefits are limited by diagnostic imaging limitations, such as resolution and area coverage.
Are There Alternatives to Dental X-Rays for Oral Health Diagnosis?
Yes, digital imaging techniques like intraoral photography and optical coherence tomography can serve as alternatives to dental x-rays, reducing radiation exposure while still effectively diagnosing oral health issues.
Can Pregnant Women Safely Undergo Dental X-Rays?
Yes, pregnant women can safely undergo dental x-rays. Modern techniques greatly minimize radiation exposure, ensuring fetal safety. Nevertheless, dental professionals typically use leaded aprons and thyroid collars to further protect the patient and fetus from unnecessary exposure.
What Is the Cost Typically Associated With Dental X-Rays?
The cost of dental X-rays varies based on location and insurance coverage, typically ranging from $25 to $250. The frequency of X-rays, often annually, can also impact the overall dental care expenses.
How Should I Care for My Mouth After Receiving a Dental X-Ray?
Post X-ray care primarily involves continuing routine oral hygiene practices. Brush and floss regularly, rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash, and maintain a balanced diet to guarantee ideal oral health following a dental X-ray.